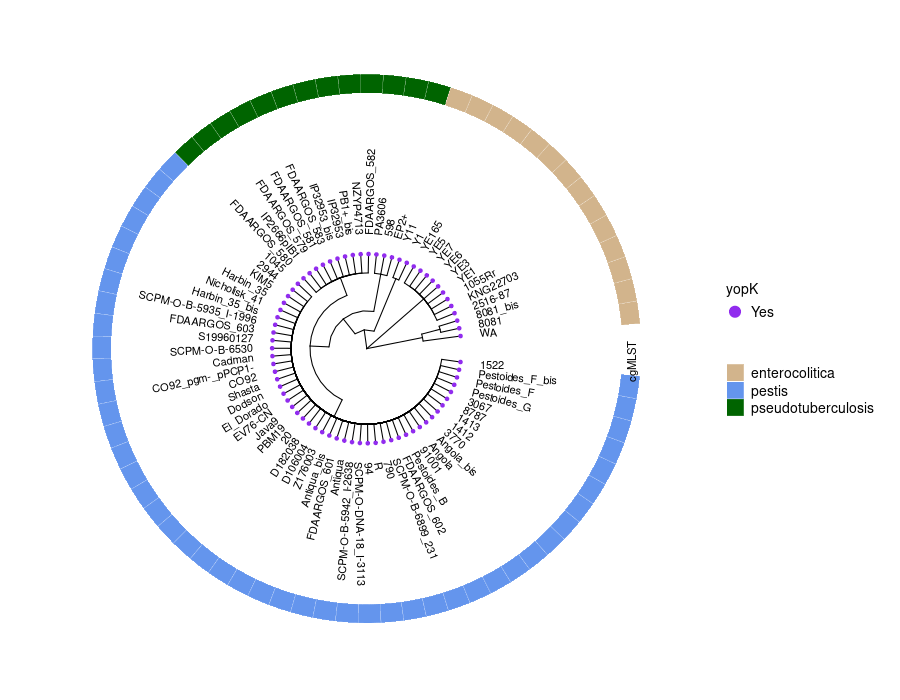
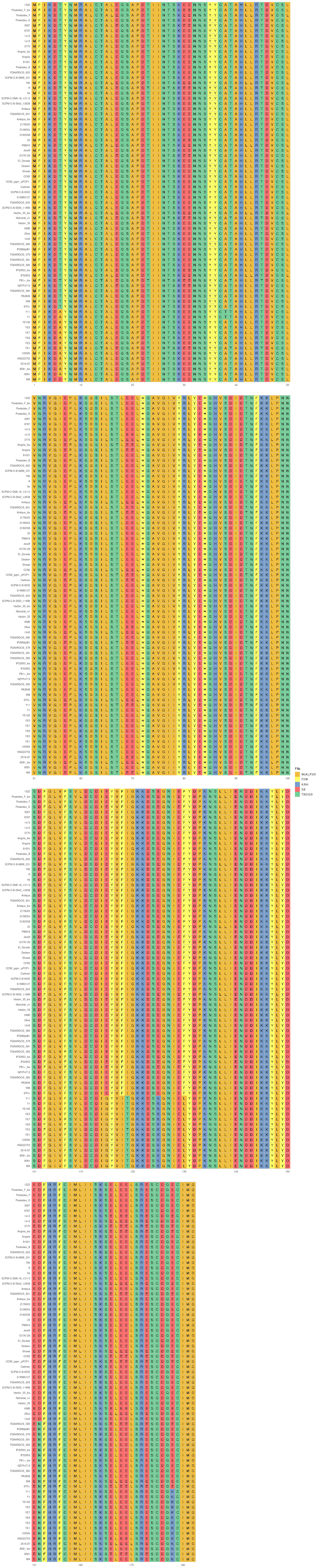
Plot phylogenetic tree_heatmap and MSA on yopBDJTEMKOH[NR]
gene_x 0 like s 1684 view s
Tags: plot, python, R, processing, scripts
| x | y | | ------------ | ------------ | | x | y | | x | y |
|Isolate|yopJ|yopB|yopT|yopE|yopD|yopM|yopK|yopO|yopH| | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | |Yersinia_enterocolitica_1055Rr|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_2516-87|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_8081|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_8081_bis|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_KNG22703|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_WA|1|1|1|1|1|0|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_Y1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_Y11|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_YE1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_YE165|1|1|1|1|0|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_YE3|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_YE5|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_YE6|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_enterocolitica_YE7|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_1045|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_1412|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_1413|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_1522|1|1|0|0|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_20|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_2944|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_3067|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_3770|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_790|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_pestis_8787|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_91001|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_94|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Angola|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Angola_bis|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Antiqua|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Antiqua_bis|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_CO92|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_CO92_pgm-_pPCP1-|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Cadman|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_D106004|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_D182038|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Dodson|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_EV76-CN|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_El_Dorado|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_FDAARGOS_601|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_pestis_FDAARGOS_602|0|1|1|1|1|0|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_FDAARGOS_603|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Harbin_35|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Harbin_35_bis|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Java9|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_pestis_KIM5|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Nicholisk_41|1|1|1|0|1|1|1|0|1| |Yersinia_pestis_PBM19|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Pestoides_B|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Pestoides_F|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Pestoides_F_bis|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Pestoides_G|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_R|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_S19960127|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_SCPM-O-B-5935_I-1996|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_SCPM-O-B-5942_I-2638|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_SCPM-O-B-6530|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_SCPM-O-B-6899_231|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_SCPM-O-DNA-18_I-3113|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Shasta|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pestis_Z176003|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_598|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_EP2+|0|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_FDAARGOS_579|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_FDAARGOS_580|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_FDAARGOS_581|1|1|1|0|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_FDAARGOS_582|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_FDAARGOS_583|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_IP2666pIB1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_IP32953|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_IP32953_bis|1|1|1|1|0|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_NZYP4713|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_PA3606|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1|1| |Yersinia_pseudotuberculosis_PB1+_bis|1|1|1|1|1|0|1|1|1|
-
This step uses rsync to download data from the NCBI server to a local directory, save all gff-files in the directory prokka.
rsync --copy-links --recursive --times --verbose rsync://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/GCF/001/696/305/GCF_001696305.1_UCN72.1 Yersinia_pestis_1045 -
The step processes GFF files containing gene annotations for a set of samples in the directory prokka. The primary goal is to modify the GFF files and create new ones with specific changes and to save them in the directory prokka_plus. The script operates on each sample one by one, and for each sample, it performs the following steps:
- Replace all occurrences of \tCDS\t with CDS in the original GFF file.
- Extract all lines containing CDS and save them in a new file with the suffix _CDS.gff.
- Replace all occurrences of ID= with ID_old= in the new _CDS.gff file.
- Cut the second field (delimited by ;) from the _CDS.gff file and save it in a new file with the suffix _CDS_f2.
- Replace all occurrences of Parent=gene- with ID= in the _CDS_f2 file.
- Paste the contents of the CDS.gff and _CDS_f2 files side by side, with a ; delimiter, and save the result in a new file with the suffix _CDS.gff.
-
Run the enum.py script on the CDS.gff file to add line numbers at the end, and save the result in a new file with the suffix _CDS__.gff. import sys
if len(sys.argv) < 2: print("Please provide a filename as an argument.") sys.exit(1) filename = sys.argv[1] try: with open(filename) as f: for i, line in enumerate(f): print(f"{line.strip()}_{i+1}") except FileNotFoundError: print(f"File {filename} not found.") -
Extract all lines from the original GFF file that do not contain CDS and save them in a new file with the suffix _nonCDS.gff.
- Remove all lines containing ### from the nonCDS.gff file and save the result in a new file with the suffix _nonCDS.gff.
- Concatenate the contents of the nonCDS.gff and _CDS__.gff files and save the result in a new file with the suffix _nonCDS_CDS.gff.
- Replace all occurrences of CDS with \tCDS\t in the _nonCDS_CDS.gff file.
- Append the string ##FASTA to the end of the _nonCDS_CDS.gff file.
- Modify the FASTA file associated with the sample by replacing the first field (delimited by a space) with the corresponding sample name.
- Concatenate the modified GFF file (_nonCDS_CDS.gff) and the modified FASTA file, and save the result in the ../prokka_plus/ directory with a new name based on the sample name.
- After processing all samples, the script removes intermediate files generated during the process.
for sample in Yersinia_pestis_1045 Yersinia_pestis_SCPM-O-B-6291_C-25 Yersinia_pestis_2944 Yersinia_pestis_KIM10+ Yersinia_pestis_M-1482; do sed -i 's/\tCDS\t/_CDS_/g' ${sample}.gff grep "_CDS_" ${sample}.gff > ${sample}_CDS.gff sed -i 's/ID=/ID_old=/g' ${sample}_CDS.gff cut -d';' -f2 ${sample}_CDS.gff > ${sample}_CDS_f2 sed -i 's/Parent=gene-/ID=/g' ${sample}_CDS_f2 paste -d';' ${sample}_CDS.gff ${sample}_CDS_f2 > ${sample}_CDS_.gff python enum.py ${sample}_CDS_.gff > ${sample}_CDS__.gff # add a line number to end to avoid the sameple Gene_ID grep -v "_CDS_" ${sample}.gff > ${sample}_nonCDS.gff grep -v "###" ${sample}_nonCDS.gff > ${sample}_nonCDS_.gff cat ${sample}_nonCDS_.gff ${sample}_CDS__.gff > ${sample}_nonCDS_CDS.gff sed -i 's/_CDS_/\tCDS\t/g' ${sample}_nonCDS_CDS.gff echo "##FASTA" >> ${sample}_nonCDS_CDS.gff cut -d' ' -f1 ../assembly/${sample}.fna > ../assembly/${sample}.fasta; cat ${sample}_nonCDS_CDS.gff ../assembly/${sample}.fasta > ../prokka_plus/$(echo $sample | cut -d'_' -f3- | tr " " "_").gff; done rm *_CDS.gff *_CDS_f2 *_CDS_.gff *_CDS__.gff *_nonCDS.gff *_nonCDS_.gff
-
This step runs Roary, a tool for pan-genome analysis. It takes annotated bacterial genomes in GFF3 format as input and clusters the genes based on sequence similarity.
roary -p 4 -f ./roary -i 95 -cd 99 -s -e -n -v prokka_plus/1045.gff prokka_plus/SCPM-O-B-6291_C-25.gff prokka_plus/2944.gff prokka_plus/KIM10+.gff -
This step extracts the coding sequences (CDS) of specific genes from multiple genome files and saves them to an output file. Start-files: roary/pan_genome_reference.fa and roary/gene_presence_absence.csv
#grep "yopT" roary/gene_presence_absence.csv > yopT_seq.txt for gene_id in M486_RS20945_3996 YE105_RS20560_4012; do for gbff in Yersinia_massiliensis_2011N-4075/GCF_013282765.1_ASM1328276v1/GCF_013282765.1_ASM1328276v1_genomic.gbff.gz Yersinia_pestis_EV_NIIEG/GCF_000590535.2_ASM59053v2/GCF_000590535.2_ASM59053v2_genomic.gbff.gz Yersinia_pestis_Shasta/GCF_000834335.1_ASM83433v1/GCF_000834335.1_ASM83433v1_genomic.gbff.gz Yersinia_ruckeri_NVI-492/GCF_023212565.2_ASM2321256v2/GCF_023212565.2_ASM2321256v2_genomic.gbff.gz Yersinia_pestis_Pestoides_G/GCF_000834985.1_ASM83498v1/GCF_000834985.1_ASM83498v1_genomic.gbff.gz; do output=$(python3 extract_CDS_of_a_locus_tag.py ${gbff} $(echo "${gene_id}" | cut -d '_' -f 1-2)) if [[ ! -z "${output}" ]]; then gbff_short=$(echo "${gbff}" | cut -d '/' -f 1) printf "%s\t%s\n" "${gbff_short}" "${output}" >> yopT_seq.txt fi done done #-- code snippet of extract_CDS_of_a_locus_tag.py -- from Bio import SeqIO import sys import gzip #python3 extract_CDS_of_a_locus_tag.py GCF_001188735.1_ASM118873v1_genomic.gbff.gz M486_RS20950 # Get the file name from the command-line argument if len(sys.argv) == 3: filename = sys.argv[1] locus_tag = sys.argv[2] else: print(sys.argv) print("Error: no file name provided") sys.exit(1) # Open the compressed file and read the sequences with gzip.open(filename, "rt") as f: # Open the GenBank file and read the first record # record = SeqIO.read("GCF_001188735.1_ASM118873v1_genomic.gbff", "genbank") for record in SeqIO.parse(f, "genbank"): #print("%s %i" % (record.id, len(record))) # Define the locus_tag you want to extract #locus_tag = "M486_RS20950" # Loop through the features and extract the CDS with the specified locus_tag for feature in record.features: if feature.type == "CDS" and "locus_tag" in feature.qualifiers and feature.qualifiers["locus_tag"][0] == locus_tag: # Extract the CDS location information and sequence location = feature.location seq = location.extract(record).seq #print(f">{locus_tag}") print(f"{seq}") # Translate the nucleotide sequence to protein sequence #protein_seq = seq.translate() #print(f"Locus tag: {locus_tag}\nProtein sequence: {protein_seq}") -
The given code converts a DNA sequence file to a protein sequence file, aligns the protein sequences using MAFFT or MUSCLE, and constructs a phylogenetic tree using FastTree.
#mafft --clustalout --adjustdirection yopK_seqs.fasta > yopK_seqs.output #fasttree -gtr -gamma -nt yopK_alignment.fasta > yopK_alignment.tree #raxml-ng --all --model GTR+G+ASC_LEWIS --prefix core_gene_raxml --threads 6 --msa yopK_alignment_.fasta --bs-trees 1000 -slow #fasttree <input_file> > <output_file> for yop in yopJ yopB yopT yopE yopD yopM yopK yopO yopH; do python3 ../../../plotTreeHeatmap/dna_to_protein.py ${yop}_seq.txt ${yop}_protein.fasta python3 ../../../plotTreeHeatmap/protein_alignment.py ${yop}_protein.fasta ${yop}_aligned_protein.fasta mafft awk -F '_' '/^>/ { printf(">%s", $3); for (i = 4; i <= NF; ++i) printf("_%s", $i); printf("\n"); next } { print }' ${yop}_aligned_protein.fasta > ${yop}_aligned_protein_.fasta done fasttree yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta > yopE_aligned_protein.tree fasttree yopO_aligned_protein_.fasta > yopO_aligned_protein.tree fasttree yopT_aligned_protein_.fasta > yopT_aligned_protein.tree grep ">" yopE_aligned_protein.fasta > typing_yopE.csv grep ">" yopO_aligned_protein.fasta > typing_yopO.csv grep ">" yopT_aligned_protein.fasta > typing_yopT.csv #-- construct typing_for yopE -- cut -f1 -d'_' typing_yopE.csv > f1 cut -f2 -d'_' typing_yopE.csv > f2 cut -f3- -d'_' typing_yopE.csv > f3_ paste f3_ typing_yopE.csv > temp1 paste f1 f2 > temp2 paste temp1 temp2 > typing_yopE_.csv #Isolate,Name,Genus,Species,yopE #R,Yersinia_pestis_R,Yersinia,pestis,Yes #20,Yersinia_pestis_20,Yersinia,pestis,Yes #... #-- for yopO -- cut -f1 -d'_' typing_yopO.csv > f1 cut -f2 -d'_' typing_yopO.csv > f2 cut -f3- -d'_' typing_yopO.csv > f3_ paste f3_ typing_yopO.csv > temp1 paste f1 f2 > temp2 paste temp1 temp2 > typing_yopO_.csv #-- for yopT -- cut -f1 -d'_' typing_yopT.csv > f1 cut -f2 -d'_' typing_yopT.csv > f2 cut -f3- -d'_' typing_yopT.csv > f3_ paste f3_ typing_yopT.csv > temp1 paste f1 f2 > temp2 paste temp1 temp2 > typing_yopT_.csv # code snippet of dna_to_protein.py from Bio import SeqIO from Bio.Seq import Seq from Bio.SeqRecord import SeqRecord import sys def translate_dna_to_protein(dna_fasta_file, protein_fasta_file): protein_records = [] for record in SeqIO.parse(dna_fasta_file, "fasta"): protein_seq = record.seq.translate(to_stop=True) protein_record = SeqRecord(protein_seq, id=record.id, description=record.description) protein_records.append(protein_record) SeqIO.write(protein_records, protein_fasta_file, "fasta") if __name__ == "__main__": input_file = sys.argv[1] output_file = sys.argv[2] translate_dna_to_protein(input_file, output_file) # code snippet of protein_alignment.py import sys from Bio.Align.Applications import MafftCommandline, MuscleCommandline from Bio import SeqIO from Bio import AlignIO def run_alignment(input_file, output_file, aligner): if aligner.lower() == "mafft": mafft_cline = MafftCommandline(input=input_file) stdout, stderr = mafft_cline() elif aligner.lower() == "muscle": muscle_cline = MuscleCommandline(input=input_file, out=output_file) stdout, stderr = muscle_cline() else: print("Invalid aligner. Please choose 'mafft' or 'muscle'.") sys.exit(1) with open(output_file, "w") as aligned_fasta: aligned_fasta.write(stdout) if __name__ == "__main__": if len(sys.argv) < 4: print("Usage: python protein_alignment.py input_fasta output_fasta aligner") print("Example: python protein_alignment.py input_protein.fasta aligned_protein.fasta mafft") sys.exit(1) else: input_fasta = sys.argv[1] output_fasta = sys.argv[2] aligner_choice = sys.argv[3] run_alignment(input_fasta, output_fasta, aligner_choice) -
This step generates a circular phylogenetic tree, a heatmap, and a multiple alignment sequence in a single figure. The tree is constructed from the aligned protein sequence "yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta" and the heatmap is based on the "typing_yopE_.csv" data. The multiple alignment sequence is added into the final figure by extracting specific sequences from the aligned protein sequence file.
library(ggtree) library(ggplot2) library(Biostrings) library(stringr) library(dplyr) library(ape) library(ggmsa) #install.packages("cowplot") library(cowplot) setwd("/home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics/plotTreeHeatmap/") # -- edit tree -- #https://icytree.org/ #0.000780 #info <- read.csv("typing_198.csv") info <- read.csv("typing_yopE_.csv") info$name <- info$Isolate #rownames(info) <- info$name info$yopE <- factor(info$yopE) #tree <- read.tree("core_gene_alignment_fasttree_directly_from_186isoaltes.tree") --> NOT GOOD! #tree <- read.tree("raxml.tree") #tree <- read.tree("yopK_alignment_modified.tree") tree <- read.tree("yopE_aligned_protein.tree") #tree <- read.tree("core_gene_raxml.raxml.bestTree") cols <- c(Yes='purple2', No='skyblue2') # -- tree -- tree_plot <- ggtree(tree, layout='circular', branch.length='none') %<+% info + scale_color_manual(values=cols) + geom_tiplab2(aes(label=name), offset=1) + geom_tippoint(aes(color=yopE)) #+ scale_color_manual(values=cols) + geom_tiplab2(aes(label=name), offset=1) #, geom='text', align=TRUE, linetype=NA, hjust=1.8,check.overlap=TRUE, size=3.3 #difference between geom_tiplab and geom_tiplab2? #+ theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, vjust = 0.5)) + theme(axis.text = element_text(size = 20)) + scale_size(range = c(1, 20)) #font.size=10, png("ggtree2.png", width=1260, height=1260) #png("ggtree.png", width=1000, height=1000) #svg("ggtree.svg", width=1260, height=1260) tree_plot dev.off() # -- heatmap -- #heatmapData2 <- info %>% select(Isolate, cgMLST, Lineage) heatmapData2 <- info %>% select(Isolate, Species) rn <- heatmapData2$Isolate heatmapData2$Isolate <- NULL heatmapData2 <- as.data.frame(sapply(heatmapData2, as.character)) rownames(heatmapData2) <- rn #"1","2","3","4","9","12","13","14","16","18", "19","30","32","36","39","41","42","43","44","53", "64","79","83","84","92","140","148","154","171","172", "173","194","215","217","252","277","279","282","290","312", "335","NA" #https://bookdown.org/hneth/ds4psy/D-3-apx-colors-basics.html #"blue","cyan", "skyblue2", "azure3","blueviolet","darkgoldenrod", "tomato","mediumpurple4","indianred", #"cornflowerblue","darkgreen","seagreen3","tan","red","green","orange","pink","brown","magenta", "cornflowerblue","darkgreen","red","tan","brown", #heatmap.colours <- c("cornflowerblue","darkgreen","seagreen3","tan","red", "navyblue", "gold", "lightcyan3","green","orange","pink","purple","magenta","brown", "darksalmon","chocolate4","darkkhaki", "maroon","lightgreen", "darkgreen","seagreen3","tan","red", "navyblue", "gold", "green","orange","pink","purple","magenta","brown", "darksalmon","chocolate4","darkkhaki", "lightcyan3", "maroon","lightgreen", "darkgrey") #names(heatmap.colours) <- c("pestis","pseudotuberculosis","similis","enterocolitica","frederiksenii","kristensenii","occitanica","intermedia","hibernica","canariae","alsatica","rohdei","massiliensis","bercovieri","aleksiciae","mollaretii","aldovae","ruckeri","entomophaga", "1","1Aa","1B","2","2/3-9a","2/3-9b","4","5","6","8","10","11","12","13","14","16","17","29","NA") heatmap.colours <- c("cornflowerblue","darkgreen","seagreen3","tan","red", "navyblue", "gold", "lightcyan3","green","orange","pink","purple","magenta","brown", "darksalmon","chocolate4","darkkhaki", "maroon","lightgreen") names(heatmap.colours) <- c("pestis","pseudotuberculosis","similis","enterocolitica","frederiksenii","kristensenii","occitanica","intermedia","hibernica","canariae","alsatica","rohdei","massiliensis","bercovieri","aleksiciae","mollaretii","aldovae","ruckeri","entomophaga") #"cornflowerblue","darkgreen","seagreen3","tan","red","green","orange","pink","brown","magenta","cornflowerblue", #"2.MED","4.ANT","2.ANT","1.ORI","1.IN","1.ANT","0.ANT3","0.PE4","0.PE3","0.PE2","1a", #mydat$Regulation <- factor(mydat$Regulation, levels=c("up","down")) #rochesterensis-->occitanica png("ggtree_and_gheatmap_yopE.png", width=1000, height=800) #png("ggtree_and_gheatmap.png", width=1290, height=1000) #png("ggtree_and_gheatmap.png", width=1690, height=1400) #svg("ggtree_and_gheatmap.svg", width=1290, height=1000) #svg("ggtree_and_gheatmap.svg", width=17, height=15) tree_heatmap_plot <- gheatmap(tree_plot, heatmapData2, width=0.2,colnames_position="top", colnames_angle=90, colnames_offset_y = 0.1, hjust=0.5, font.size=4, offset = 8) + scale_fill_manual(values=heatmap.colours) + theme(legend.text = element_text(size = 14)) + theme(legend.title = element_text(size = 14)) + guides(fill=guide_legend(title=""), color = guide_legend(override.aes = list(size = 5))) tree_heatmap_plot dev.off() #samtools faidx yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta "1522" > yopE_aligned_protein_sorted.fasta #samtools faidx yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta "Pestoides_F_bis" >> yopE_aligned_protein_sorted.fasta #... #samtools faidx yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta "8081" >> yopE_aligned_protein_sorted.fasta #samtools faidx yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta "WA" >> yopE_aligned_protein_sorted.fasta #https://bioconductor.org/packages/devel/bioc/vignettes/ggtreeExtra/inst/doc/ggtreeExtra.html #https://github.com/YuLab-SMU/supplemental-ggmsa #https://github.com/YuLab-SMU/ggmsa library(ggmsa) library(ggplot2) library(ggtree) #library(gggenes) library(ape) library(Biostrings) library(ggnewscale) library(dplyr) library(ggtreeExtra) library(phangorn) library(RColorBrewer) library(patchwork) library(ggplotify) library(aplot) library(magick) library(treeio) #data <- "../supplemental-ggmsa-main/data/s_RBD.fasta" data <- "yopE_aligned_protein_.fasta" #data <- "yopE_aligned_protein_sorted.fasta" #dms <- read.csv("data/DMS.csv") #del <- c("expr_lib1", "expr_lib2","expr_avg","bind_lib1","bind_lib2") #dms <- dms[,!colnames(dms) %in% del] tidymsa <- tidy_msa(data) #tidymsa <- assign_dms(tidymsa, dms) #Mapping the position to the protein-protein interaction plot #tidymsa$position <- tidymsa$position + 330 #dms = TRUE, png("alignment_yopE.png", width=1100, height=5400) msa_plot <- ggplot() + geom_msa(data = tidymsa, char_width = 0.5, seq_name = TRUE, show.legend = TRUE) + theme_msa() + facet_msa(50) #scale_fill_gradientn(name = "ACE2 binding", colors = c(colRD(75),colBU(25))) msa_plot dev.off() # #Combine the ggtree and ggmsa plots using the cowplot package: # combined_plot <- cowplot::plot_grid(msa_plot, tree_heatmap_plot, ncol = 1, align = "v", axis = "l", rel_heights = c(3, 2)) # ggsave("combined_plot.png", combined_plot, width = 10, height = 10, dpi = 300)
点赞本文的读者
还没有人对此文章表态
本文有评论
没有评论
看文章,发评论,不要沉默
最受欢迎文章
- Motif Discovery in Biological Sequences: A Comparison of MEME and HOMER
- Calling peaks using findPeaks of HOMER
- Kraken2 Installation and Usage Guide
- Why Do Significant Gene Lists Change After Adding Additional Conditions in Differential Gene Expression Analysis?
- Should the inputs for GSVA be normalized or raw?
- PiCRUST2 Pipeline for Functional Prediction and Pathway Analysis in Metagenomics
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- pheatmap vs heatmap.2
- Setup conda environments
- Guide to Submitting Data to GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus)
最新文章
- Risks of Rebooting into Rescue Mode
- 足突(Podosome)、胞外囊泡(Extracellular Vesicle)与基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)综合解析
- NCBI BioSample Submission Strategy for PJI and Nasal Microbiota Study
- Human RNA-seq processing for Data_Ben_RNAseq_2025
最多评论文章
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The top 10 genes
- Retrieving KEGG Genes Using Bioservices in Python
推荐相似文章
MicrobiotaProcess Group2 vs Group6 (v1)