Small RNA-seq analysis pipeline XICRA
gene_x 0 like s 904 view s
Tags: pipeline
https://github.com/cougarlj/COMPSRA/issues/18
https://github.com/HCGB-IGTP/XICRA
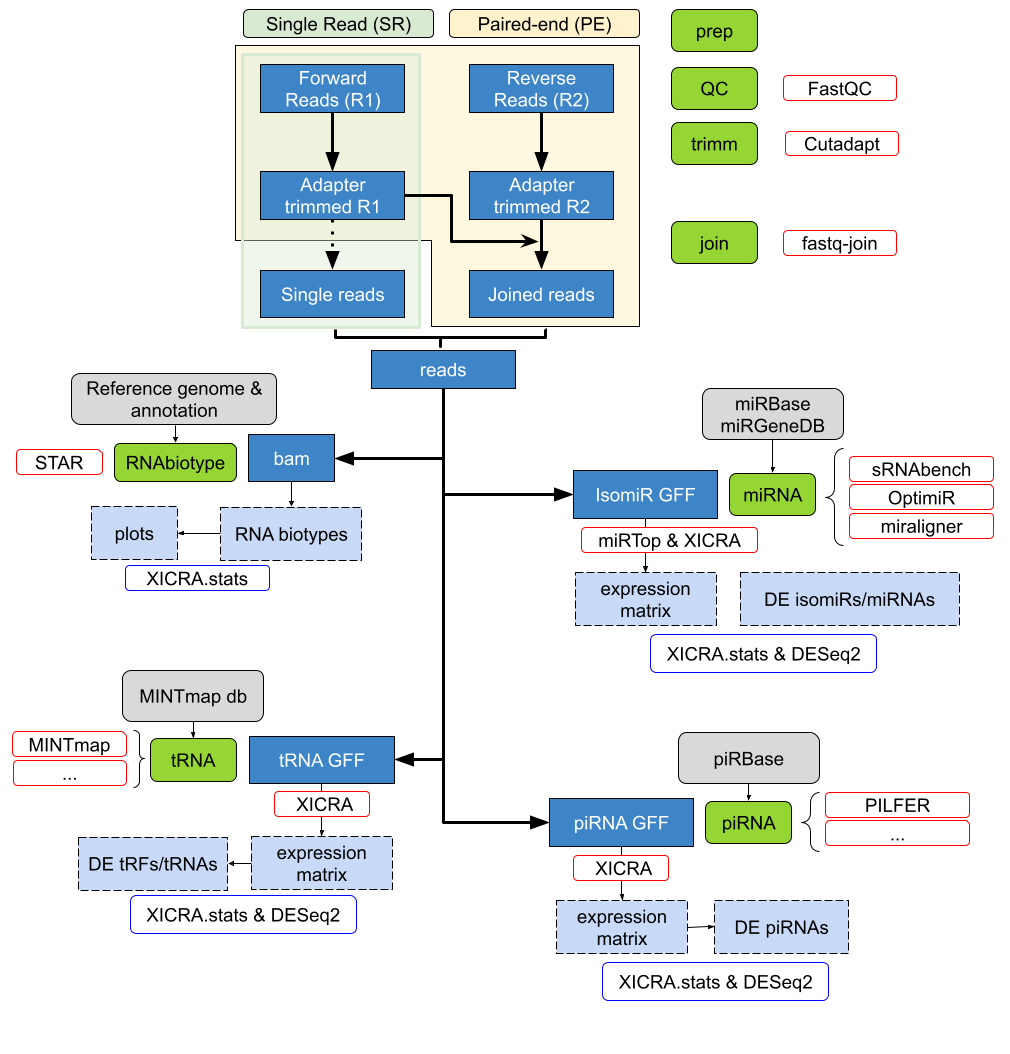
- This pipeline is designed to take paired end reads in fastq format, trim adapters and low-quality base pairs positions, and merge read pairs (R1 & R2) that overlap.
- A mapping step to the reference genome (user defined) assigns joined reads to all major RNA biotypes including miRNA and isomiRs, tRNA fragments (tRFs) and piwi associated RNAs (piRNAs).
- Then, XICRA produces a miRNA analysis at the isomiR level using joined reads, with several choices of software that can be selected by the user with standardized output.
- Results are generated for each sample, analyzed and summarized for all samples in a single expression matrix.
- This information can be processed at the miRNA or isomiR level (single sequence) but also summarizing for each isomiR variant type.
- Statistical summaries can be easily accessed using the accompanied R package XICRA.stats (https://github.com/HCGB-IGTP/XICRA.stats).
-
Although the pipeline is designed to take paired-end reads, it also accepts single-end reads.
-
XICRA uses cutadapt [30] for the adapter trimming analysis.
- Default trimming preset parameter settings are: to keep all reads regardless of whether the adapter is found or not, a 10% maximum adapter matching error rate (mismatches, insertions and deletions), and a 3 bp minimum overlap length.
- User must provide specific adapter sequences for the trimming analysis.
- An optional previous quality checking step can be performed for each sample using FastQC [31] before the trimming analysis.
-
Results are summarized for all samples using MultiQC software [32].
-
Once all reads are adapter trimmed, the tool uses fastq-join from ea-utils [33] to join the two PE reads, if provided, on the overlapping ends.
- Apart from the joined reads, this tool also generates two files with the R1 and R2 reads that cannot be joined.
- As a default the minimum overlap is set to 6 bp and the maximum allowed difference for the reads to be joined is set to 0% to retain 100% matching read pairs ensuring high quality sequencing information.
-
Parameters can be modified using the different options provided.
-
The XICRA pipeline can continue to process either joined PE reads or SR reads.
- Two levels of mapping are implemented. The first level profiles RNA biotypes using STAR [34] to map reads against the reference genome and featureCounts [35] to extract and quantify numbers of reads by class. The second level focuses specifically on small RNA subclasses.
-
Here we describe the miRNA analysis implemented within XICRA but the modularity and versatility of the pipeline would make it quite straightforward to include other RNA biotypes analyses in detail.
-
For miRNAs analysis at the isomiR resolution level, XICRA allows the user to use either miraligner [26], sRNAbench from sRNAtoolbox [27] or OPTIMIR [28].
- Each software uses different strategies and might produce different results [36].
- We have included them as they allow following standardization procedures performed by miRTOP software and adopt the miR.gff3 file format [37].
- Again, the pipeline modular implementation would allow adding additional softwares converging and adapting to miRTOP and miR.gff3 format.
- For each of the softwares mentioned above and included within the miRNA module in XICRA default parameters are used.
- Some of these parameters can be modified using the different options provided.
- As a result of this miRNA module, annotation is generated that categorizes isomiRs into classes based on their sequence modifications (including iso_5p, iso_3p, iso_add, iso_snv, iso_snv_seed, iso_snv_central_offset, iso_snv_central, iso_snv_central_suppl) following miRTOP suggested classification scheme.
- A final conversion step from individual per sample miR.gff3 files into a single expression matrix is performed.
- This file serves as input for differential expression (DE) analysis.
- Information is provided for each unique sequence and indexed names contain the miRNA, the variant type and license plate (unique identifier, UID) provided by miRTOP.
- Duplicated entries at the sequence level, produced by different modifications from the same or different miRNA are discarded.
-
An additional matrix is provided containing the sequence information for each encrypted UID.
-
Per sample read count matrices at the isomiR level are summarized into a single expression matrix that it serves as input for DE analysis between the comparison groups of interest.
- We have generated an additional R package (XICRA.stats) that facilitates the retrieval of these matrices and parses the information included within each unique index name provided.
- The DE analysis can be done aggregating data at the mature miRNA level (i.e. hsa-miR-501-3p), by isomiR class (i.e. hsa-miR-501-3p_iso_5p), by specific length variant cluster (i.e. hsa-miR-501-3p_iso_3p:-2) or with the sequence of the read itself as the counting data.
- This is useful since different types of modification may coexist in a single sequence, and non-templated additions and internally edited sequences can differ leading to isomiRs that can fall into different categories or be derived from different mature miRNAs.
- DE analysis is performed outside of the tool with DESeq2 package in R [38].
Types of small RNAs
-
miRNA(微小RNA):微小RNA是长度约为20-24个核苷酸的短RNA分子,它们在基因表达的后转录水平上发挥调控作用。miRNA通过结合到mRNA分子的互补序列上,可以抑制翻译过程或导致mRNA的降解。miRNA参与许多细胞过程,包括发育、分化和细胞周期控制。
-
tRNA(转运RNA):转运RNA是长约70-90个核苷酸的适配器分子,在蛋白质生物合成的翻译过程中起着关键作用。它们负责将相应的氨基酸运送到核糖体,并通过其反密码子环识别mRNA上的密码子,确保在形成的蛋白质中正确排序氨基酸。
-
piRNA(Piwi相互作用RNA):Piwi相互作用RNA是一类长度通常在24至31个核苷酸之间的小RNA分子,主要存在于动物的生殖细胞中,参与转座子沉默和基因组稳定性。它们与Piwi蛋白互作,帮助抑制转座元件的转录,保护基因组完整性。
-
snRNA(小核RNA):小核RNA是一组在真核生物细胞核中发现的小RNA分子,长度约为100-200个核苷酸。它们是剪接体的重要组成部分,剪接体是负责从前mRNA分子中移除内含子的复合体。
-
snoRNA(小核仁RNA):小核仁RNA是发现在细胞的核仁中的特化RNA分子,长度约为60-300个核苷酸。它们参与rRNA的修饰和成熟过程,特别是rRNA的化学修饰过程,如甲基化和伪尿苷化。
-
circRNA(环形RNA):环形RNA是一种具有闭合圆形结构的RNA,没有常见的5'和3'端。它们可以由外显子或内含子产生,并具有多种功能,包括作为miRNA的分子海绵、影响转录和调节基因表达。CircRNAs参与许多生物学过程,并与各种疾病有关。
在生物学研究中,进行差异表达分析通常用于比较不同样本或条件下RNA分子的表达水平变化。对于上面RNA类型:
-
miRNA(微小RNA):进行差异表达分析是有意义的。miRNAs在调控基因表达和参与多种生物过程中扮演关键角色,因此,分析其在不同条件下的表达差异有助于了解其在疾病发生、发展或其他生物学过程中的功能。
-
tRNA(转运RNA):虽然tRNAs是蛋白质合成中必不可少的,但它们在不同状态下的表达量差异通常不是研究的主要焦点。尽管如此,tRNA的改变有时可以反映细胞的代谢状态或应对压力的能力,但这并不是差异表达分析的常见应用。
-
piRNA(Piwi-interacting RNA):进行差异表达分析同样有意义,尤其是在研究生殖细胞、干细胞和癌症等领域。piRNAs与转座子的沉默和基因组稳定性维护有关,因此分析其差异表达有助于揭示它们在这些过程中的作用。
-
snRNA(小核RNA)和snoRNA(小核仁RNA):这两种RNA主要参与RNA加工和修饰,如剪接和rRNA的修饰。通常情况下,对它们进行差异表达分析不是很常见,因为它们更多地涉及基本的细胞内过程。然而,如果研究的目的是特定RNA加工途径的变化,那么它们的表达分析可能是有意义的。
-
circRNA(环状RNA):进行差异表达分析是有意义的。circRNAs与许多生理过程有关,包括作为miRNA的海绵、影响基因的转录和参与疾病的发展。因此,分析circRNAs的表达差异可以帮助理解它们在不同生物学背景下的功能和作用。
总的来说,miRNA、piRNA和circRNA的差异表达分析在许多研究领域是有意义的,因为它们在疾病和生物学过程中的角色。而tRNA、snRNA和snoRNA的差异表达分析可能不那么常见,除非研究特定的生物过程或条件下它们的特定变化。
通过将 cDNA 测序读段映射到人类基因组上,我们能否确定这些读段是否来源于 circRNA?
可以通过将 cDNA 的 reads 映射到人类基因组上来帮助确定它们是否来源于 circRNA。在 circRNA 的研究中,这种映射过程中寻找的关键特征是反向剪接事件,也就是说,寻找那些正常线性剪接顺序被反向连接的 reads。
在标准的基因表达研究中,mRNA 被逆转录成 cDNA,然后生成的测序 reads 通常会映射到基因组的连续区域以表示线性剪接事件。然而,对于 circRNA,由于它们是由反向剪接形成的,因此具有独特的“头尾相连”的结构。在测序数据中,这些反向剪接或“头尾相连”的事件会导致 reads 映射到基因组的非连续区域,即一个 exon 的末尾连接到另一个 exon 的开始,这与正常的线性剪接顺序不同。
通过检测这种非典型的、非连续的映射模式,可以推断出 reads 来自于 circRNA。需要专门的生物信息学工具和算法来识别这些特殊的映射模式,从而鉴定出 circRNAs。这些工具能够识别跨越独特的反向剪接点的 reads,帮助研究者确定哪些 reads 来自 circRNAs。
点赞本文的读者
还没有人对此文章表态
本文有评论
没有评论
看文章,发评论,不要沉默
最受欢迎文章
- Motif Discovery in Biological Sequences: A Comparison of MEME and HOMER
- Calling peaks using findPeaks of HOMER
- Kraken2 Installation and Usage Guide
- Why Do Significant Gene Lists Change After Adding Additional Conditions in Differential Gene Expression Analysis?
- Should the inputs for GSVA be normalized or raw?
- PiCRUST2 Pipeline for Functional Prediction and Pathway Analysis in Metagenomics
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- pheatmap vs heatmap.2
- Setup conda environments
- Guide to Submitting Data to GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus)
最新文章
- Risks of Rebooting into Rescue Mode
- 足突(Podosome)、胞外囊泡(Extracellular Vesicle)与基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)综合解析
- NCBI BioSample Submission Strategy for PJI and Nasal Microbiota Study
- Human RNA-seq processing for Data_Ben_RNAseq_2025
最多评论文章
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The top 10 genes
- Retrieving KEGG Genes Using Bioservices in Python
推荐相似文章
Processing Data_Michelle_RNAseq_2025
Setup the environment for lumicks-pylake and C_Trap-Multimer-photontrack.ipynb
🧬 Cadmium Resistance Gene Analysis in Staphylococcus epidermidis HD46
Workflow for RNA-Binding Protein Enrichment and RNA Type Distribution Analysis (Ute’s Project)