博氏疏螺旋体在宿主细胞内的摄取与处理机制
gene_x 0 like s 845 view s
Tags: research, technique
https://grk2771.de/phd-students-2/
Project 2 Summary (Interplay between Yersinia enterocolitica and the autophagosomal/lysosomal system in epithelial host cells and organoids, 耶尔森菌与上皮宿主细胞和类器官中的自噬体/溶酶体系统的相互作用)
- Yersinia enterocolitica engages a cell-invasive strategy to colonize the host intestinal tissue.
- The intracellular, invasive phenotype depends on the Yersinia outer membrane protein invasin which binds and activates eukaryotic beta-1-integrin receptors to promote uptake of the bacteria into infected host cells.
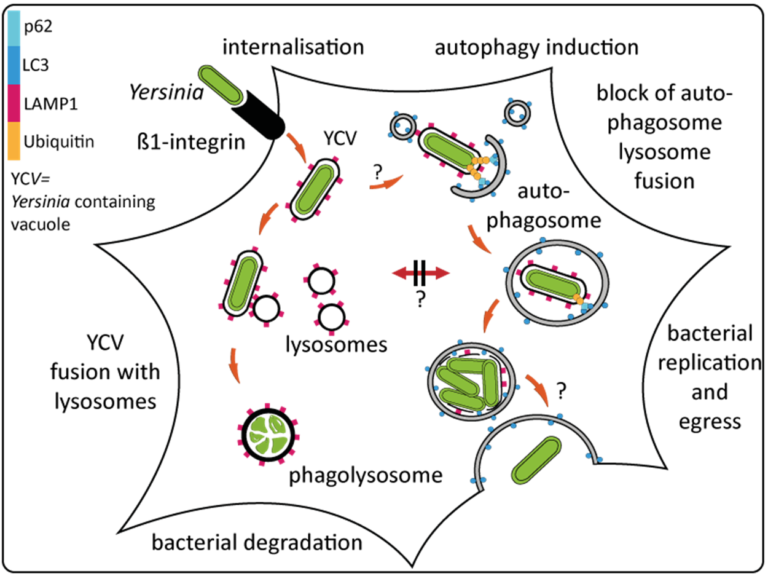
- Our previous studies have shown that internalization of Yersinia by epithelial cells results in the formation of two distinct populations of intravacuolar bacteria.
- One part of the ingested bacteria is subjected to the endosomal / phagolysosomal pathway in which the Yersinia-containing vacuoles (YCVs) fuse with lysosomes and the enclosed bacteria are eliminated.
- The second half of the bacteria ends up in vacuoles with autophagy-related characteristics, displaying recruitment of autophagosomes, phagophore formation, and xenophagy.
- Importantly, fusion of these autophagic vacuoles with lysosomes is actively prevented by Yersinia which results in intracellular survival and proliferation of Yersinia in the non-acidified, autophagic compartments.
- This indicates that Y. enterocolitica takes advantage of the macroautophagy pathway to gain access to an intracellular niche that enables bacterial replication in a protected compartment.
- Eventually, this leads to bacterial egress from the infected cells.
- The molecular mechanisms that direct Yersinia to autophagosomes and prevent fusion with lysosomes are, however, presently unclear.
- Our project consequently aims to explore the intracellular lifestyle of Yersinia in order to uncover novel principles in bacterial pathogenesis and in the regulation of vesicle function and trafficking pathways in infected epithelial host cells.
- The autophagosomal ['fægәsәum] and lysosomal ['laisəsəum] pathways to which Yersinia is sorted are differentially characterized by proteomic and co-localization studies.
- Furthermore, the Yersinia factors that manipulate the physiological endocytic-lysosomal pathway are investigated by evaluating a transposon-based Yersinia mutation library.
- Functional approaches in molecularly modified host cells will then specify the roles of the identified pathways for Yersinia survival, replication and release from infected cells.
-
We expect the results of this work to be of general importance for cell and human infection biology.
-
Yersinia enterocolitica 通过细胞侵入策略定殖宿主肠组织。
- 这种细胞内侵入表型依赖于耶尔森菌外膜蛋白入侵素(invasin),该蛋白与真核β-1整合素(beta-1-integrin)受体结合并激活,从而促进细菌进入受感染的宿主细胞。
- 我们之前的研究表明,耶尔森菌被上皮细胞内化后,会形成两个不同的细胞内空泡细菌群体。
- 部分吞噬的细菌会被引导至内体/吞噬溶酶体途径(endosomal / phagolysosomal pathway),其中含有耶尔森菌的空泡(YCVs)与溶酶体(lysosomes)融合,包裹的细菌被消灭。
- 另一部分细菌最终进入具有自噬相关特征的空泡,表现出自噬体招募、吞噬泡形成和异噬现象(autophagy-related characteristics, displaying recruitment of autophagosomes, phagophore formation, and xenophagy)。
- 重要的是,耶尔森菌主动阻止这些自噬空泡与溶酶体的融合,从而在未酸化的自噬隔室中存活并增殖。
- 这表明耶尔森菌利用巨自噬途径获得一个使细菌在受保护隔室内复制的细胞内生态位。
- 最终,这导致细菌从受感染的细胞中释放出来。
- 然而,指导耶尔森菌进入自噬体并防止其与溶酶体融合的分子机制目前尚不清楚。
- 因此,我们的项目旨在探索耶尔森菌的细胞内生活方式,以揭示细菌致病机制和受感染上皮宿主细胞中囊泡功能及运输途径调控的新原理。
- 通过蛋白质组学和共定位研究,分别表征耶尔森菌被引导至的自噬体和溶酶体途径(autophagosomal ['fægәsәum] and lysosomal ['laisəsəum] pathways)。
- 此外,通过评估一个基于转座子的耶尔森菌突变文库 (transposon-based Yersinia mutation library),研究操纵生理性内吞-溶酶体途径的耶尔森菌因子。
- 然后,通过在分子上修改的宿主细胞中进行功能性方法研究,明确这些途径在耶尔森菌存活、复制和从受感染细胞中释放的角色。
- 我们预计该研究的结果将对细胞和人类感染生物学具有普遍的重要性。
- endocytic[ˏendәu'sitik]生内吞作用的
Project 1 Summary
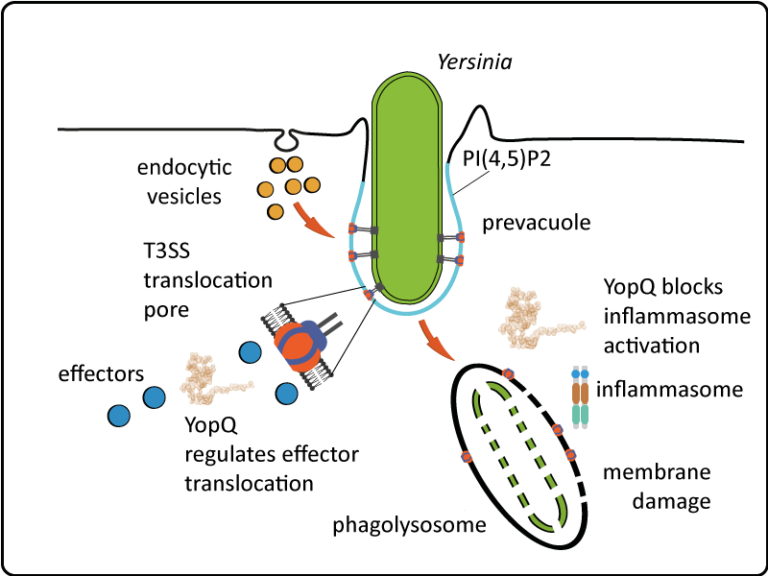
- The T3SS/injectisome of Yersinia enterocolitica is a molecular machine that injects effector proteins into host cells to support the bacterial infection strategy.
- The injectisome directly connects to host cells via a translocon/pore complex, that serves as an entry gate for the effectors.
- Simultaneously attached to the T3SS needle tip and integrated into the host cell membrane, the translocon is subject to multi-layered regulation by bacterial and host cell factors. YopQ/YopK is a Yersinia effector that controls both, activity and immune recognition of the translocon from within the host cells.
- Despite the critical role of YopQ/YopK in function and immune recognition of the Yersinia translocon, its direct interaction partners and molecular mode of action are unknown.
- The overall goal of P1 is to determine the molecular mode by which Y. enterocolitica YopQ controls activity and immune recognition of the T3SS translocon. To this end, i) the dynamics of bacterially translocated YopQ in host cells and its correlation with function, formation, degradation and/or immune sensing of the translocon will be visualized at the highest spatial and temporal resolution; ii) the macrophage interaction partners of YopQ/YopK will be identified by affinity purification and verified in functional assays, and iii) the structure-function relationship of YopQ in terms of its intracellular spatiotemporal dynamics, interaction with binding partners, and effects on translocon activity and immune recognition will be investigated.
-
Methods to be applied include: sCRISPR/Cas mediated mutagenesis and gene editing of Yersinia; affinity purification and mass spectrometric analysis of host-pathogen protein complexes; in vitro protein-protein interaction; super-resolution fluorescence microscopy of bacterial and host proteins in fixed and living macrophages.
-
耶尔森菌的T3SS/注射体是一种分子机器,可以将效应蛋白注入宿主细胞,以支持细菌的感染策略。
- 注射体通过转位子/孔复合物直接与宿主细胞连接,作为效应物进入的入口。
- 同时附着在T3SS针尖并整合到宿主细胞膜中的转位子受到细菌和宿主细胞因素的多层调控。YopQ/YopK是控制转位子在宿主细胞内活动和免疫识别的耶尔森菌效应物。
- 尽管YopQ/YopK在耶尔森菌转位子功能和免疫识别中起着关键作用,其直接的相互作用伙伴和分子作用机制尚不清楚。 P1的总体目标是确定耶尔森菌YopQ控制T3SS转位子活动和免疫识别的分子机制。为此,i) 将以最高的空间和时间分辨率可视化细菌转移到宿主细胞内的YopQ的动态及其与转位子的功能、形成、降解和/或免疫感知的相关性;ii) 通过亲和纯化识别YopQ/YopK的巨噬细胞相互作用伙伴,并在功能性测定中验证;iii) 调查YopQ在其细胞内时空动态、与结合伙伴的相互作用以及对转位子活动和免疫识别的影响方面的结构-功能关系。
- 应用的方法包括:sCRISPR/Cas介导的耶尔森菌突变和基因编辑;宿主-病原体蛋白复合物的亲和纯化和质谱分析;体外蛋白-蛋白相互作用;固定和活巨噬细胞中细菌和宿主蛋白的超分辨率荧光显微镜。
Project 7 Summary
- Human Polyomaviruses (PyV) are highly prevalent and establish a lifelong asymptomatic persistence in the healthy immunocompetent host1,2.
- However, under immunosuppression, these viruses can reactivate, causing life-threatening infections (e.g. BKV caused PyV associated nephropathy, PVAN) due to uncontrolled viral replication1.
- Currently, no specific antiviral treatment is available. This lack of effective therapeutics is partly due to the lack of small animal models and the availability of only poor surrogate in vitro/in vivo systems.
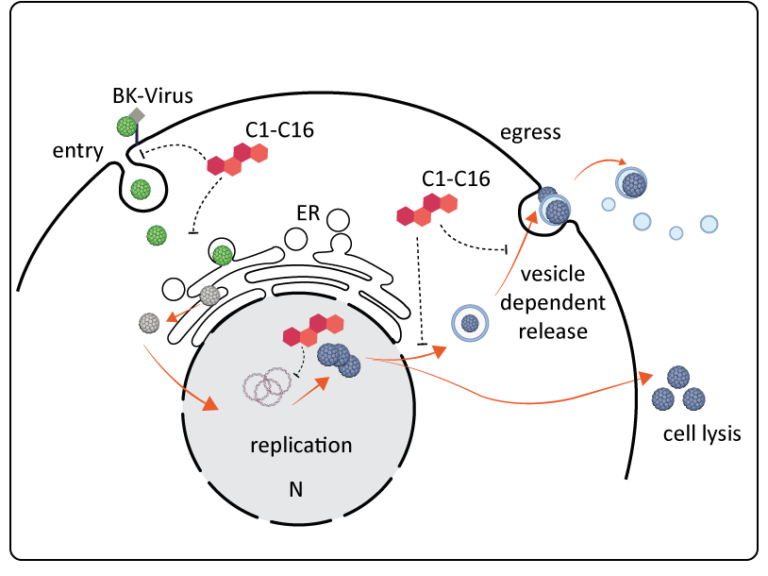
- We have recently identified 16 small molecule inhibitors, C1-16, against BKV using a phenotypic high throughput screen (Kraus et al., unpublished).
- For the further development of these inhibitors, it is essential to have an understanding of their cellular target structure and/or which part of the viral life cycle they inhibit.
- Within this project we will gain a better understanding of the BKV the life cycle in relevant infection systems (e.g. primary cells and organoids).
- We will use these previously identified antiviral compounds in terms of their interference with essential host structures for viral reproduction (transport vesicles, nuclear uptake, replication compartments or vesicle dependent egress).
- Furthermore, we will characterize specific viral inhibitors at the molecular and structural level.
- The project uses organoids and primary cells as infection models and BKV inhibitor characterization.
- It applies confocal live cell microscopy to follow BKV entry/spread.
-
Furthermore, the project takes advantage of X-ray crystallography to characterize inhibitor/target interaction.
-
人类多瘤病毒(Polyomaviruses,简称PyV)具有高度流行性,并在健康的免疫健全宿主中建立终生的无症状持续感染。
- 然而,在免疫抑制的情况下,这些病毒可能会重新激活,导致由于病毒失控复制而引起的致命感染(例如,由BKV引起的与多瘤病毒相关的肾病,PVAN)。
- 目前,没有特定的抗病毒治疗方法。这种缺乏有效治疗手段的部分原因是缺乏小型动物模型以及仅有不良替代的体外/体内系统。
- 我们最近通过表型高通量筛选(Kraus等,未发表)鉴定出16种针对BKV的小分子抑制剂,C1-16。
- 为了进一步开发这些抑制剂,了解其细胞靶结构和/或其抑制病毒生命周期的哪一部分是至关重要的。
- 在这个项目中,我们将更好地理解BKV在相关感染系统中的生命周期(例如,原代细胞和类器官)。
- 我们将使用这些先前鉴定的抗病毒化合物,研究它们对病毒复制所需的关键宿主结构(如运输小泡、核摄取、复制区或依赖小泡的出芽)的干扰。
- 此外,我们将在分子和结构水平上表征特定的病毒抑制剂。
- 该项目使用类器官和原代细胞作为感染模型,并对BKV抑制剂进行表征。
- 它应用共聚焦活细胞显微镜来追踪BKV的进入/传播。
- 此外,该项目利用X射线晶体学来表征抑制剂/靶标的相互作用。
Project 4 Summary
The Role of CEP55 in exosomal section by ovarian cancer cells
- Borrelia burgdorferi is the causative agent of Lyme disease, a multisystemic disorder affecting skin, nervous system and joints.
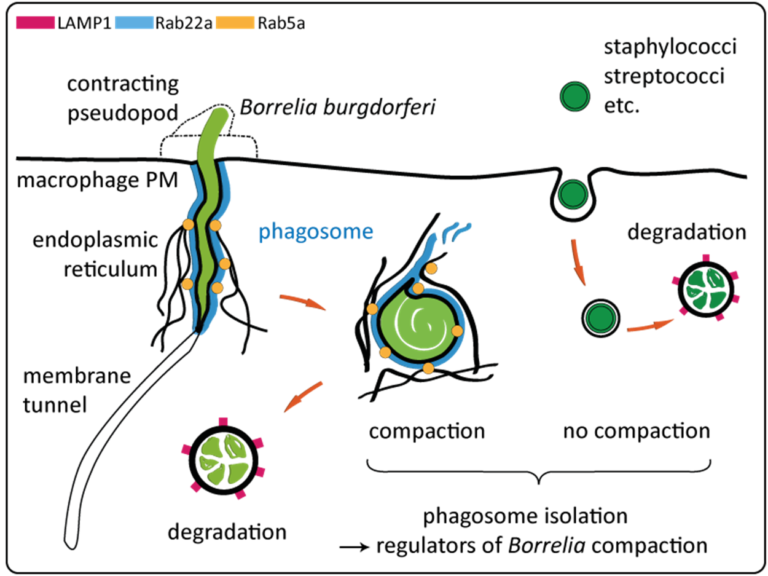
- Uptake and intracellular processing of borreliae by host cells proceed in several steps:
- i) immobilisation of highly motile borreliae by formin-regulated filopodia1,3,
- ii) enwrapment by a coiling pseudopod, regulated by the formin Daam1 and Arp2/3 complex1,2,
- iii) uptake into a Rab22a-positive phagosome, which is contacted by Rab5a-positive vesicles in an ER-dependent manner2,
- iv) compaction of borreliae by reduction of the phagosome surface through membrane tubulation2,4,
- v) degradation in mature phago-lysosomes2,4 (see also Fig.).
- We also identified lipids such as PI(3)P and phosphatidylserine that play specific roles during uptake and processing of borreliae4,5.
- Moreover, we recently discovered that membrane tunnels, a novel phagocytic structure, extend deeper into the host cell cytoplasm than the bacteria-containing part of phagosomes, probably due to partial extrication of highly motile borreliae (see Fig.).
- This shows that internalisation of borreliae by macrophages is a unique and highly dynamic process, whose outcome depends on a tug-of-war between spirochetes and host cells5.
- Notably, both phagosomes and tunnels form multiple STIM1-positive ER contact sites, pointing to a role of ER-connected processes, including regulation of Ca2+ influx, in the maturation of borreliae containing phagosomes5.
- However, the roles of ER contact sites and specifically phagosomal Ca2+ influx in borreliae phagosome maturation are currently unclear.
- To address these questions, and to identify Borrelia-specific regulators of phagosome compaction and maturation, we have established magnetic labelling of borreliae, permitting subsequent purification of phagosomes. Results from these experiments will identify novel targets for modulation of intracellular processing of spirochetes in human immune cells.
- This project will
- a) analyse the proteome and lipidome of Borrelia-containing phagosomes and tunnels,
- b) characterise ER contact sites at phagosomes and tunnels on a molecular and functional level, and
- c) identify regulators that are specific for compaction of spirochetes, as opposed to bacteria without pronounced phagosomal compaction such as staphylococci and streptococci, or which follow different strategies for intracellular survival or persistence such as Yersinia, Legionella or Salmonella.
-
SILAC labelling of macrophages will be combined with chemical crosslinking, (co-) immunoprecipitation and proximity labelling assays to identify ligands on the Borrelia surface involved in recruiting the molecular machinery driving phagosome/tunnel closure and phagosome compaction. Lattice light sheet microscopy and focused ion beam microscopy will be used to analyse membrane flow at phagosomes and tunnels.
LAMP1(溶酶体相关膜蛋白1)是一个在溶酶体功能和维护中起关键作用的蛋白质。以下是关于LAMP1的详细介绍: 功能: 溶酶体膜蛋白: LAMP1主要位于溶酶体的膜上,溶酶体是细胞内负责降解和回收各种生物分子的细胞器。 细胞内运输: LAMP1帮助溶酶体与其他细胞室的融合和运输,确保大分子的正确处理。 内吞作用和自噬: LAMP1参与内吞作用(细胞摄取外部物质)和自噬(细胞内部成分的降解)。 细胞表面标记物: LAMP1也可以作为细胞研究中的溶酶体标记物,用于追踪溶酶体的活动。 结构: 糖蛋白: LAMP1是糖蛋白,即它具有附加的糖分子,这些糖链对其功能和稳定性至关重要。 跨膜结构: 它通过跨膜域穿越溶酶体膜,细胞质部分朝向溶酶体内部。 临床相关性: 溶酶体储存病: LAMP1的突变或功能失调可能与溶酶体储存病有关,这种病症中溶酶体不能正常降解物质。 癌症研究: LAMP1的表达水平有时可以作为癌症研究中的标记,因为其水平在不同类型的癌症中可能有所不同。 总的来说,LAMP1对溶酶体功能和细胞稳态至关重要。 -
博氏疏螺旋体是引起莱姆病的病原体,这是一种影响皮肤、神经系统和关节的多系统疾病。
-
宿主细胞对疏螺旋体的摄取和细胞内处理过程包括几个步骤:
-
i) 通过formin调控的丝状伪足将高度运动的疏螺旋体固定,
- ii) 由formin Daam1和Arp2/3复合物调节的螺旋伪足包裹,
- iii) 被Rab22a阳性吞噬体摄取,后者通过依赖ER的方式与Rab5a阳性小泡接触,
- iv) 通过膜管化减少吞噬体表面使疏螺旋体压缩,
-
v) 在成熟的吞噬溶酶体中降解(参见图示)。
-
我们还发现了在疏螺旋体摄取和处理过程中发挥特定作用的脂类,如PI(3)P和磷脂酰丝氨酸。
- 此外,我们最近发现膜隧道(一种新型吞噬结构)深入宿主细胞胞质,比含细菌的吞噬体部分延伸得更深,可能是由于高度运动的疏螺旋体的部分抽离(参见图示)。
- 这表明巨噬细胞对疏螺旋体的内化是一个独特且高度动态的过程,其结果取决于螺旋体和宿主细胞之间的拉锯战。
- 值得注意的是,吞噬体和隧道都形成多个STIM1阳性的ER接触位点,表明ER连接过程(包括Ca2+内流调节)在含疏螺旋体的吞噬体成熟中的作用。
- 然而,ER接触位点的作用及吞噬体Ca2+内流在疏螺旋体吞噬体成熟中的具体作用尚不清楚。
- 为了解决这些问题,并识别疏螺旋体特异性调节吞噬体压缩和成熟的因素,我们已经建立了疏螺旋体的磁标记,从而允许随后纯化吞噬体。这些实验的结果将识别出在人体免疫细胞中调节螺旋体细胞内处理的新靶点。
-
该项目将:
-
a) 分析含疏螺旋体的吞噬体和隧道的蛋白质组和脂质组,
- b) 在分子和功能水平上表征吞噬体和隧道的ER接触位点,
-
c) 识别特异性调节螺旋体压缩的因子,相对于没有显著吞噬体压缩的细菌(如葡萄球菌和链球菌),或者采取不同细胞内生存或持久性策略的细菌(如耶尔森菌、军团菌或沙门氏菌)。
-
将结合巨噬细胞的SILAC标记与化学交联、(共同)免疫沉淀和邻近标记实验,以识别参与招募驱动吞噬体/隧道关闭和吞噬体压缩的分子机器的疏螺旋体表面配体。晶格光片显微镜和聚焦离子束显微镜将用于分析吞噬体和隧道的膜流动。
疏螺旋体摄取和细胞内处理的分子机制: 疏螺旋体在宿主细胞内的摄取和处理涉及哪些具体的分子通路?特别是formin、Daam1和Arp2/3复合物在这一过程中具体如何调控? 在疏螺旋体摄取和处理过程中,PI(3)P和磷脂酰丝氨酸分别发挥了什么具体作用? 膜隧道结构的功能和形成机制: 新发现的膜隧道结构是如何形成的?其形成机制与疏螺旋体的高运动性之间有什么关系? 这些膜隧道在疏螺旋体与宿主细胞的相互作用中起到了什么具体作用? ER接触位点在吞噬体成熟中的作用: ER接触位点(STIM1阳性)的形成机制是什么?它们在含疏螺旋体吞噬体的成熟过程中起到了什么具体作用? 吞噬体Ca2+内流在疏螺旋体吞噬体成熟中的具体作用是什么?它如何调节吞噬体的功能和疏螺旋体的降解过程? 疏螺旋体特异性吞噬体调节因子: 哪些特异性调节因子参与了疏螺旋体吞噬体的压缩和成熟?这些因子与其他细菌(如葡萄球菌、链球菌、耶尔森菌、军团菌和沙门氏菌)所需的因子有何不同? 在Borrelia感染过程中,哪些特异性调节因子和机制能够调节吞噬体的压缩和成熟,从而影响螺旋体的细胞内存活? 宿主细胞对疏螺旋体的免疫应答机制: 巨噬细胞对疏螺旋体的内化和处理过程中,宿主细胞的免疫应答是如何被调控的? 针对疏螺旋体的高运动性,宿主细胞有哪些特异性免疫防御机制? 药物靶点及治疗策略: 通过对疏螺旋体吞噬体及隧道结构的深入研究,是否可以发现新的药物靶点? 能否基于疏螺旋体特异性调节因子的研究,开发出针对莱姆病的新的治疗策略? Molecular Mechanisms of Borrelia burgdorferi Uptake and Intracellular Processing: What are the specific molecular pathways involved in the uptake and intracellular processing of Borrelia burgdorferi within host cells? Specifically, how do formin, Daam1, and the Arp2/3 complex regulate this process? What specific roles do PI(3)P and phosphatidylserine play during the uptake and processing of Borrelia burgdorferi? Function and Formation Mechanisms of Membrane Tunnels: How are the newly discovered membrane tunnels formed, and what is the relationship between their formation and the high motility of Borrelia burgdorferi? What specific roles do these membrane tunnels play in the interaction between Borrelia burgdorferi and host cells? Roles of ER Contact Sites in Phagosome Maturation: What are the mechanisms of formation for ER contact sites (STIM1-positive) and their specific roles in the maturation of Borrelia-containing phagosomes? What is the specific role of phagosomal Ca2+ influx in the maturation of Borrelia phagosomes, and how does it regulate the function of phagosomes and the degradation process of Borrelia burgdorferi? Borrelia-Specific Regulators of Phagosome Compaction and Maturation: What specific regulators are involved in the compaction and maturation of Borrelia-containing phagosomes? How do these regulators differ from those involved in the processing of other bacteria such as staphylococci, streptococci, Yersinia, Legionella, and Salmonella? During Borrelia infection, which specific regulators and mechanisms control phagosome compaction and maturation, thereby affecting the intracellular survival of Borrelia burgdorferi? Immune Response Mechanisms of Host Cells to Borrelia burgdorferi: How is the immune response of host cells regulated during the internalization and processing of Borrelia burgdorferi by macrophages? What specific immune defense mechanisms do host cells employ in response to the high motility of Borrelia burgdorferi? Drug Targets and Therapeutic Strategies: Can in-depth studies of Borrelia-containing phagosomes and membrane tunnels lead to the discovery of new drug targets? Based on research into Borrelia-specific regulators, is it possible to develop new therapeutic strategies for Lyme disease? These questions aim to delve deeply into the interaction mechanisms between Borrelia burgdorferi and host cells, potentially leading to the development of new treatment methods and improving the prevention and control of Lyme disease and related conditions. Mechanisms of Host-Pathogen Interaction: What are the key steps and molecular mechanisms involved in the uptake and intracellular processing of Borrelia burgdorferi by host cells? How do specific host cell structures and proteins, such as formins, phospholipids, and ER contact sites, contribute to the handling and degradation of Borrelia burgdorferi? Dynamics of Intracellular Pathogen Processing: What roles do newly discovered structures, like membrane tunnels, play in the intracellular journey of Borrelia burgdorferi? How does the motility of Borrelia burgdorferi influence its interaction with host cell phagosomes and subsequent intracellular processing? Cellular Defense Mechanisms: How do host immune cells, particularly macrophages, recognize, internalize, and destroy Borrelia burgdorferi? What are the cellular responses and defense mechanisms triggered by Borrelia burgdorferi infection? Phagosome Maturation and Pathogen Survival: What factors regulate the maturation of Borrelia-containing phagosomes, and how do these processes differ from those involving other pathogens? How do intracellular pathogens like Borrelia burgdorferi evade or manipulate host cell processes to ensure their survival and replication? Novel Therapeutic Targets: What potential drug targets can be identified from the molecular mechanisms involved in the uptake and degradation of Borrelia burgdorferi? How can understanding the specific interactions between Borrelia burgdorferi and host cells lead to new therapeutic strategies for Lyme disease? Role of Host Cell Structures in Infection: What is the significance of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) contact sites in the context of Borrelia burgdorferi infection, and how do they affect phagosome function and maturation? How do specific lipids and proteins on the host cell surface facilitate or hinder the intracellular processing of Borrelia burgdorferi? These questions aim to explore the broader aspects of host-pathogen interactions, intracellular processing of pathogens, and potential avenues for therapeutic intervention.
DNA virus: Papalloni-virus, Polyomavirus, Herpes-virus; RNA virus: HIV
点赞本文的读者
还没有人对此文章表态
本文有评论
没有评论
看文章,发评论,不要沉默
最受欢迎文章
- Motif Discovery in Biological Sequences: A Comparison of MEME and HOMER
- Why Do Significant Gene Lists Change After Adding Additional Conditions in Differential Gene Expression Analysis?
- Calling peaks using findPeaks of HOMER
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- pheatmap vs heatmap.2
- Should the inputs for GSVA be normalized or raw?
- Setup conda environments
- PiCRUST2 Pipeline for Functional Prediction and Pathway Analysis in Metagenomics
- Kraken2 Installation and Usage Guide
- File format for single channel analysis of Agilent microarray data with Limma?
最新文章
- Processing Data_Tam_RNAseq_2024_MHB_vs_Urine_ATCC19606
- Workflow using PICRUSt2 for Data_Karoline_16S_2025
- Viral genome assembly and recombination analysis for Data_Sophie_HDV_Sequences
- 阳光房漏水怎么办?丁基胶带才是最佳密封选择
最多评论文章
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The top 10 genes
- Retrieving KEGG Genes Using Bioservices in Python